The Lachlan catchment covers an area of 90,000 square kilometres. Nearly 1,300 kilometres of the 1,400-kilometre river is regulated by water storages, of which Wyangala Dam is the largest at 1,220 gigalitres (GL).
The river originates near Gunning in the tablelands and ends at the Great Cumbung Swamp. Important sites include the Booligal Wetlands, Lake Brewster, Lake Cowal, Great Cumbung Swamp and Lachlan Swamps, all of which are listed in the Directory of Important Wetlands in Australia.
The Lachlan catchment has important Aboriginal cultural values with environmental watering actions considering Aboriginal values and uses in consultation with communities. The Traditional Owners of the Lachlan are the Wiradjuri, Nari Nari, Ngiyampaa and Yita Yita.
Water for rivers and wetlands
In 2022–23, the focus will be to enhance natural conditions and opportunities for plants and animals to breed, move and thrive in line with ecological cues. This includes developing an adaptive watering strategy to maintain refuges and key breeding habitat to support the growth in the lower Lachlan southern bell frog population.
High flows resulting from rainfall and airspace releases have kept the Lachlan storages filling and spilling during the past 12 months. The full 350 GL of translucent flows was delivered, and the lower Lachlan floodplain system was inundated for more than 12 months.
During 2021–22, the Department of Climate Change, Energy, the Environment and Water (the department) worked with the Commonwealth Environmental Water Holder (CEWH) and stakeholders to deliver 20GL of licensed water and more than 15 GL of Environmental Water Allowance (EWA) to the lower Lachlan system.
The timing and cooperative management of environmental flows in Merrowie Creek led to Lake Tarwong filling for the first time since 2016. The active management of Lake Brewster in partnership with WaterNSW supported the largest Australian pelican breeding event for more than 30 years at the site.
Weather and water forecast
The El Niño–Southern Oscillation (ENSO) outlook remains at La Nina, with a return to neutral ENSO during winter, indicating that rainfall is likely to be above average across the catchment. All storages in the Lachlan are effectively full and are likely to continue to spill in line with rainfall–inflow events throughout winter.
Water managers have prepared watering plans that consider a range of weather and water availability scenarios in case it rains more or less than expected. This is known as resource availability scenario planning. ‘Very wet to moderate’ conditions are forecast for the Lachlan catchment in 2022–23.
1. ENSO: The interaction between the sea surface and atmosphere over the Pacific Ocean which results in dryer or wetter conditions (El Nino or La Nina).
Resource availability scenario
Current forecast: Very wet to moderate
| Conditions | Main aim | Other aims |
|---|---|---|
| Very dry | Protect | Avoid critical loss Maintain key refuges Avoid catastrophic events |
| Dry | Maintain | Maintain river functioning Maintain key functions of high priority wetlands |
| Moderate | Recover | Improve ecological health and resilience Improve opportunities for plants and animals to breed, move and thrive |
| Wet to very wet | Enhance | Restore key floodplain and wetland linkages Enhance opportunities for plants and animals to breed, move and thrive |
Key planned actions for 2022–23
Waterbirds
If required, core breeding, foraging and migratory wader habitats will be topped up in early spring and autumn to provide food and shelter for waterbirds (up to 10 GL). Water managers will make additional water (up to 10 GL) available to support bird breeding events, such as Lake Brewster pelicans.
Native fish
Water managers will deliver flows to support fish breeding and dispersal, targeting, but not limited to, continued golden perch recruitment. Flows for fish will maintain water quality in refuge systems, such as Booberoi Creek, while supporting habitat and food sources.
Vegetation
Water managers will focus on successive waterings of floodplain vegetation, lignum shrublands in Merrowie Creek and phragmites reed beds and river red gum woodland in the Great Cumbung Swamp (up to 20 GL). These watering actions will promote recovery in vegetation condition and recruitment. These sites will also contribute to waterbird and connectivity outcomes.
Additional volumes (up to 8 GL) will promote seed setting and establish inflow and outflow wetlands at Lake Brewster.
Water managers will deliver flows in the greater Cumbung region to maintain quality in-channel and wetland aquatic vegetation for southern bell frogs and to promote breeding.
Connectivity
Water managers will consider supplementing translucent flow events to extend floodplain inundation and connectivity to the river system across the lower Lachlan system (up to 40 GL), including Willandra Creek (up to 5 GL).
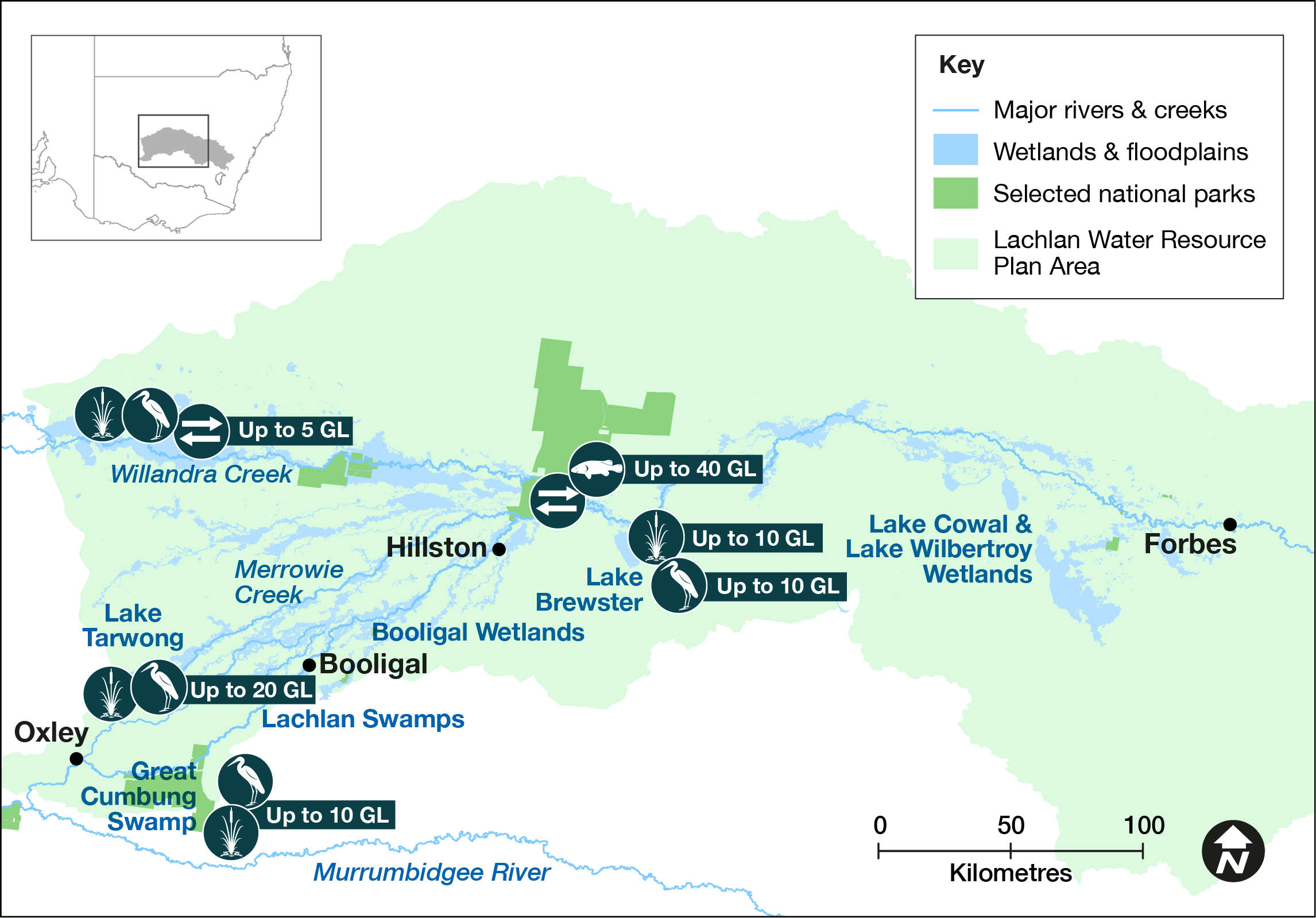
Map of proposed annual priority targets in the Lachlan Water Resource Plan area 2022–23.
The Department of Climate Change, Energy, the Environment and Water (the department) is supporting the health and resilience of rivers and wetlands by delivering water for the environment where and when it is needed. We use the best available science, management expertise and experience to manage water across the landscape. This statement of annual priorities identifies the waterways and wetlands that are likely to receive water.
Our decision-making process considers:
- expected availability of water in the coming year
- conditions of the previous year
- current health of the plants and animals in these ecosystems.
Community-based Environmental Water Advisory Groups (EWAGs) provide feedback and advice to the department on the management of water for the environment.
The NSW Government works with the Commonwealth Environmental Water Holder to manage water in the catchment.
Water for the environment is a share of the water in dams and rivers that is set aside to support the long-term health of local rivers, creeks and wetlands. Healthy rivers carry water to homes, farms, schools and businesses. Rivers and wetlands are important cultural and spiritual sites for Aboriginal people, as well as the broader community.
Planned environmental water
| Source | Maximum volume available (gigalitres) | Volume expected 1 July under current conditions (gigalitres) |
|---|---|---|
| Water quality allowance | 20 GL | 20 GL |
| Wyangala environmental water allowance | 10 GL | 10 GL |
| Lake Brewster environmental water allowance | 10 GL | 10 GL |
| Translucent flows | Up to 350 GL | Depends on significant inflows to reach triggers |
Water licenced to New South Wales
| Source | Maximum volume available (gigalitres) | Volume expected 1 July under current conditions (gigalitres) |
|---|---|---|
| General security | 37.5 GL | 37.5 GL |
| High security | 1.8 GL | 1.8 GL |
Water licenced to the Commonwealth
| Source | Maximum volume available (gigalitres) | Volume expected 1 July under current conditions (gigalitres) |
|---|---|---|
| High security | 0.9 GL | 0.9 GL |
| General security | 87 GL | 87 GL |
Notes: This is an indicative summary of expected volumes to be available. For further detail and information on available volumes you can contact the region via the Department of Climate Change, Energy, the Environment and Water on 1300 361 967.
1 gigalitre = 1000 megalitres; 2.5 megalitre = 1 Olympic swimming pool.
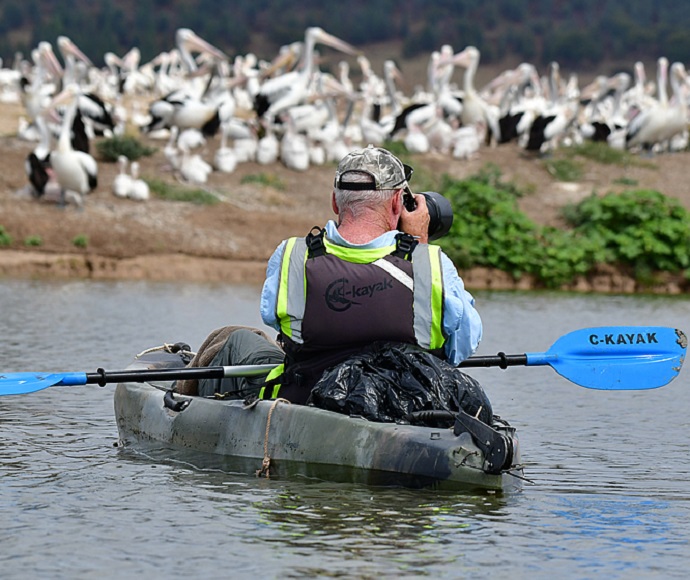

Water managers plan to make additional water available to support bird breeding events, such as for Lake Brewster pelicans.
More about ...
More information on planned and past watering events
- Lachlan Catchment – Water for the Environment: Annual Priorities 2021–22
- Lachlan catchment: Annual environmental watering priorities 2020–21
- Lachlan: Annual environmental watering priorities 2019–20
- Lachlan catchment: Annual Environmental Watering Priorities 2018–19
- Lachlan catchment: Annual environmental watering priorities 2017–18
- Lachlan Water Resource Plan Area: Statement of annual environmental watering priorities 2016–17
- Lachlan Water Resource Plan Area: Statement of annual environmental watering priorities 2015–16
- Lachlan Riverine Environmental Water Management Plan
- Water for environment outcomes 2021–22
- Use of water for the environment in NSW: Outcomes 2020–21
- Use of water for the environment in NSW: Outcomes 2019–20
- Use of water for the environment in NSW: Outcomes 2018–19
- Use of water for the environment in NSW: Outcomes 2017–18