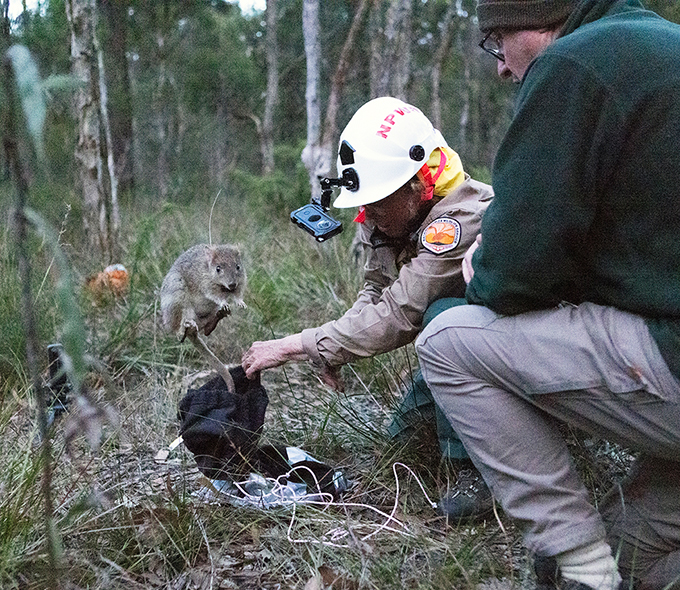
The network of feral predator-free areas is one of several actions in the NSW National Parks and Wildlife Service Threatened Species Framework to meet our commitment to zero extinctions and restore threatened species populations.
Returning locally extinct wildlife to Yiraaldiya
Formerly called Shanes Park, the new park name 'Yiraaldiya' was selected in consultation with the local Aboriginal community. The name comes from an 1899 record of the Aboriginal word that described the area between South Creek and Eastern Creek.
Yiraaldiya National Park is in western Sydney and Blacktown local government area, 40 km west-northwest of the Sydney CBD and 10 km north-east of Penrith.
Yiraaldiya National Park is 535 ha, which, combined with an additional 20 ha along the property's southern boundary, will make 555 ha of feral predator-free national park land once the project is fully established. The Blacktown Pistol Club remains on 5 ha of land reserved for this specific purpose.
The 20 ha on the southern boundary is a potential future road corridor. If Transport for NSW requires this strip of land in the future, the National Parks and Wildlife Service will be compensated under the Revocations policy.
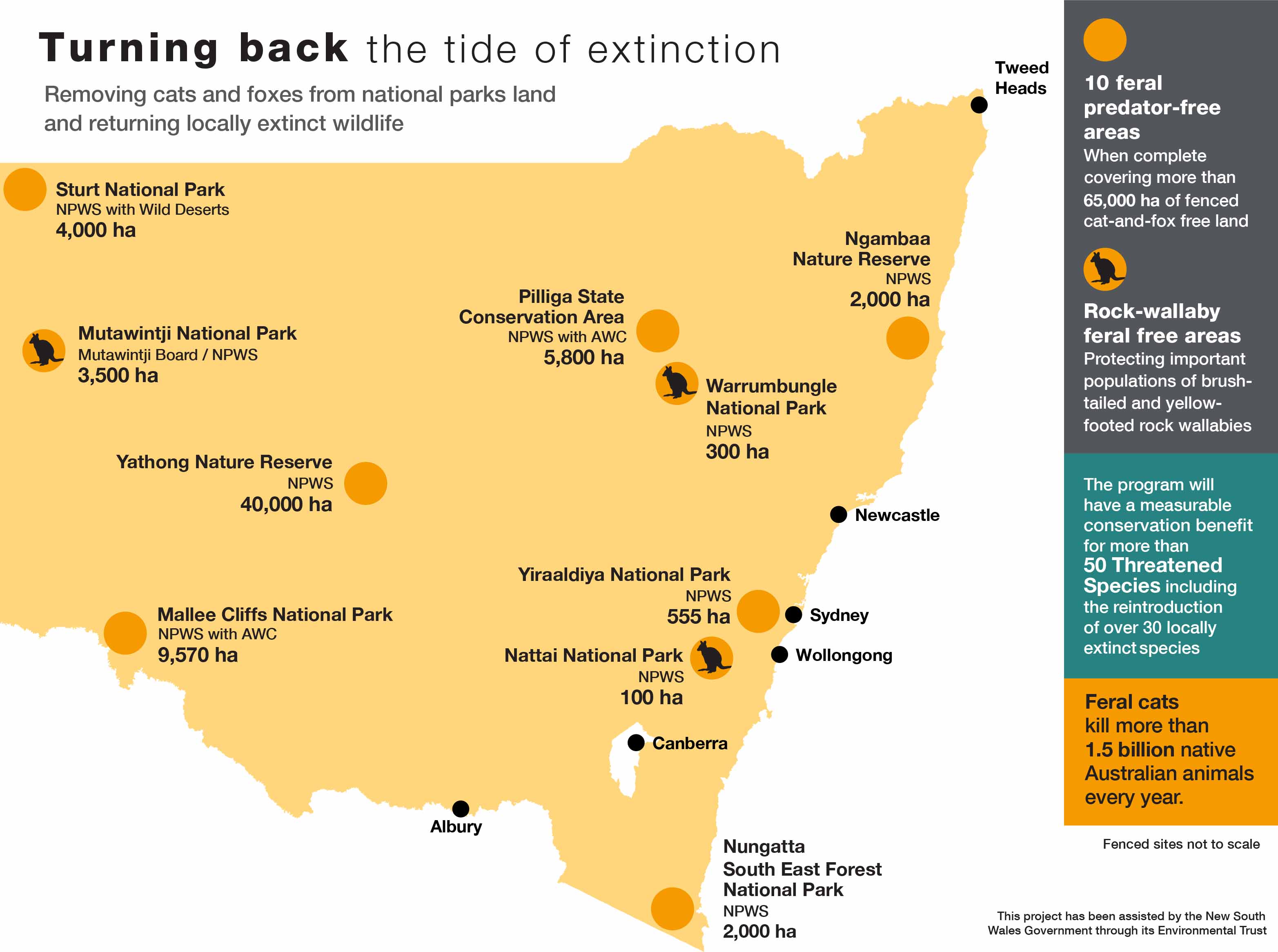
Map showing the 10 feral predator-free rewilding sites across the NSW national parks estate
How will the feral predator-free area be established?
At Yiraaldiya National Park, the establishment of the feral predator-free area involves 2 stages:
- Stage 1 – creation of a 56-ha area nested within the larger feral predator-free area. This stage is complete.
- Stage 2 – creation of the feral predator-free area encompassing 555 ha of the park. This stage is nearing completion.
The same key steps are followed for establishing each of the 10 feral predator-free areas (see Ten feral predator-free areas for more information).
The key steps at Yiraaldiya National Park are:
- building a conservation fence, establishing a boundary management trail and upgrading all other approved management trails to fire management standards
- eradicating all cats, foxes and wild dogs from within the conservation fence area
- eradicating populations of feral herbivores, including deer, goats and pigs, and maximising rabbit and hare control if eradication is not possible
- reintroduction of locally extinct animal species (previously found on the Cumberland Plain)
- monitoring, evaluation and reporting on reintroduced species and ecosystem health
- adaptive reuse and development of existing visitor infrastructure.
Relevant planning approvals are in place for the construction and operation of conservation fencing, associated infrastructure, and control of feral predators and herbivores in Yiraaldiya National Park.
Translocation plans and associated animal ethics approvals for the reintroduction of locally extinct species will occur separately.
How many animal species will be reintroduced?
Up to 30 species are being considered for reintroduction to Yiraaldiya National Park, making it one of the world's biggest urban wildlife restoration projects.
Priority species that formerly occurred in western Sydney but have become locally extinct because of feral cats and foxes are being assessed for reintroduction, including:
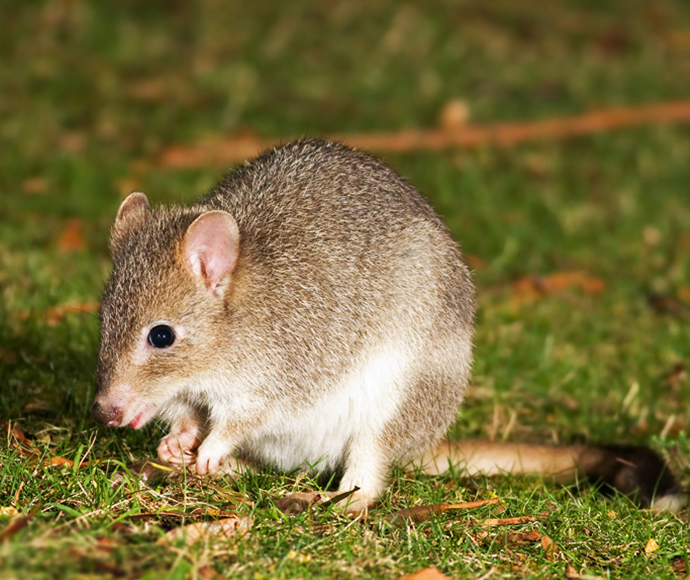
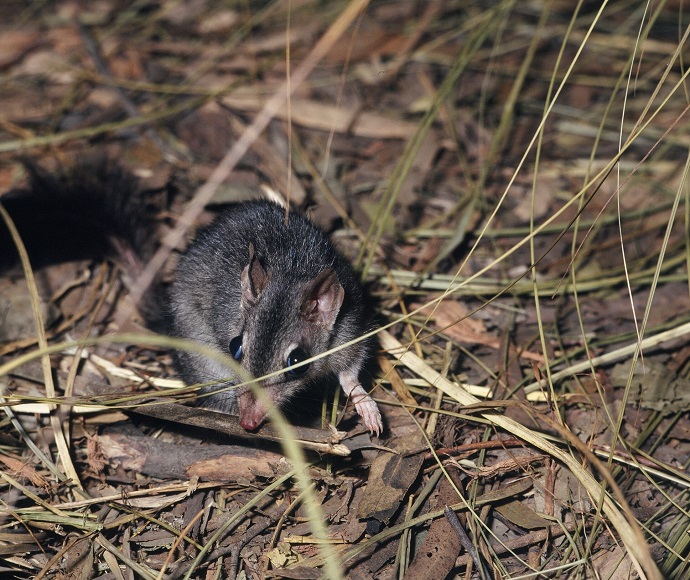
- eastern bettong
- koala
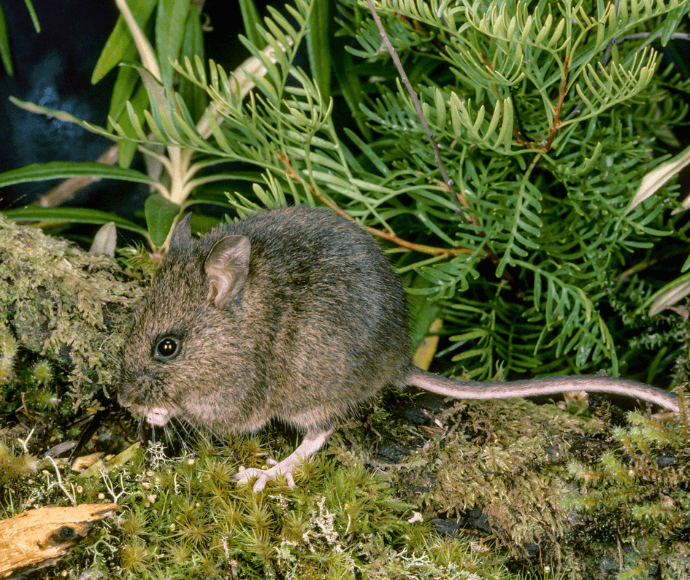
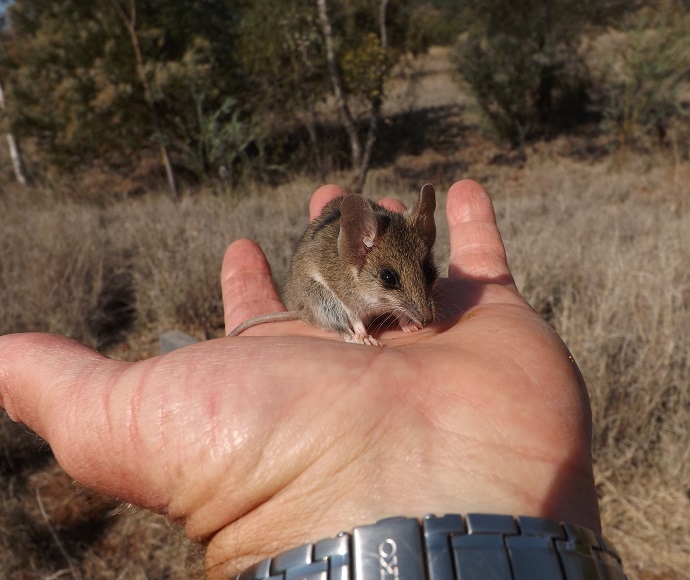
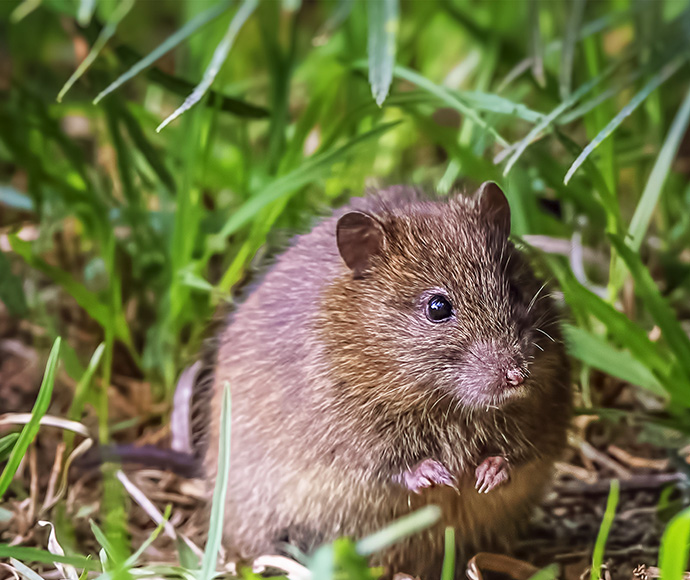
- New Holland mouse
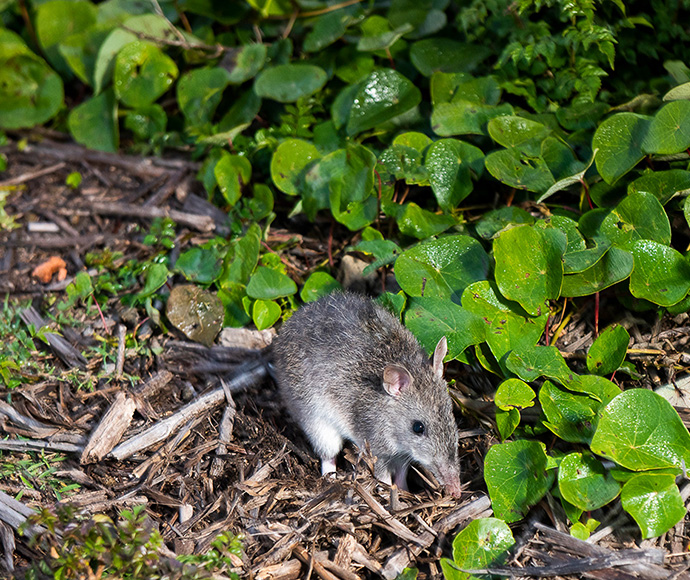
- southern long-nosed bandicoot
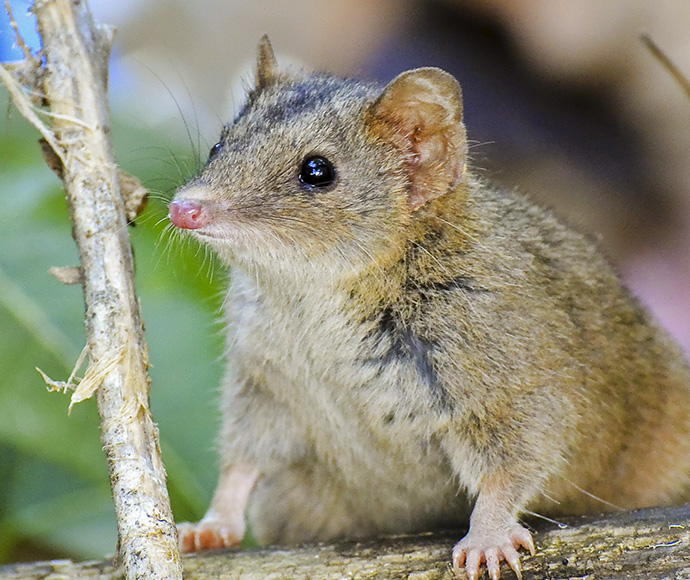
- brown antechinus
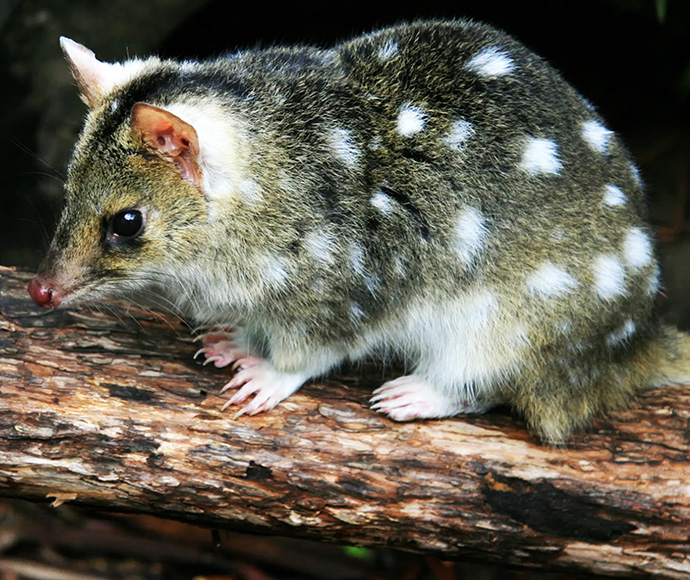
- eastern quoll
- brush-tailed phascogale
- common dunnart
- bush rat
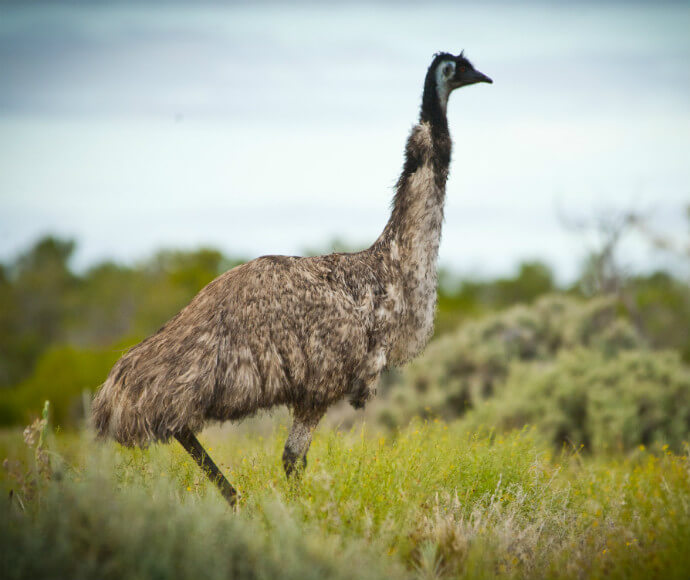
- emu
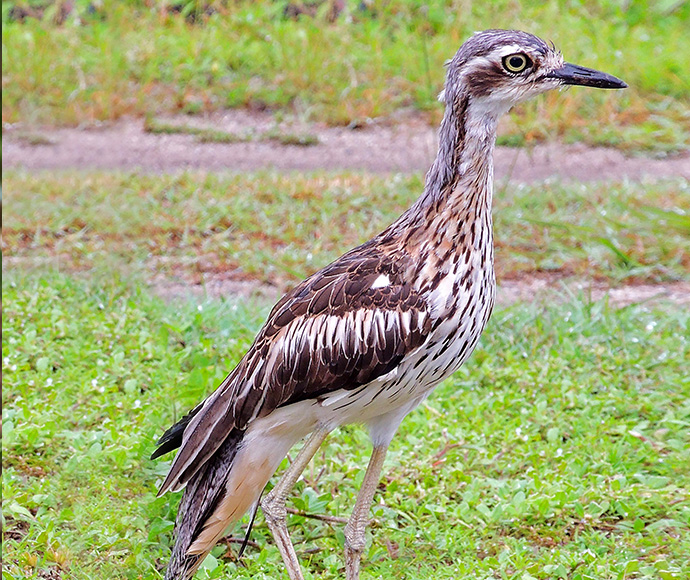
- bush stone-curlew.
Of the 30 species, up to 20 reptiles and frogs, which are now locally extinct or declining, will be considered for reintroduction to Yiraaldiya National Park.
How did we select the species for reintroduction?
All species being considered for reintroduction once lived in this location on the Cumberland Plain.
The suitability of the mammal and bird species selected for reintroduction has been confirmed by one of Australia's leading ecologists, Dr Chris Dickman, from the University of Sydney. The species list is based on specimen records, sightings, distribution modelling, reports or other accounts, and knowledge of their habitat requirements and historic ranges.
For all species except the emu, populations could be expected to increase 3- or 4-fold above the estimates provided in the report without feral cats and foxes. Such increases would likely be for mid-sized mammals such as eastern bettong and eastern quoll, as shown in other feral predator-free areas.
Species such as the eastern bettong disappeared from New South Wales over 100 years ago. The eastern quoll was last recorded in Sydney in the 1960s.
What are the other ecological benefits of the project?
The program will see the reintroduction of 'ecosystem engineer' animals. This means they play a key role in turning over soil, seed and spore dispersal, and population management through predation. Individual eastern bettongs turn over tonnes of soil every year, while eastern quolls are important predators.
The return of these ecosystem engineers will help restore the health of ecosystems at Yiraaldiya National Park.
The project will significantly improve the ecological condition of the site through:
- the removal of all feral animals
- the return of up to 30 locally extinct or declining animal species
- the restoration of ecological processes and remnant vegetation
- the effective management of fire
- the prevention of unlawful activity (formation of unauthorised tracks, waste and rubbish dumping and so on).
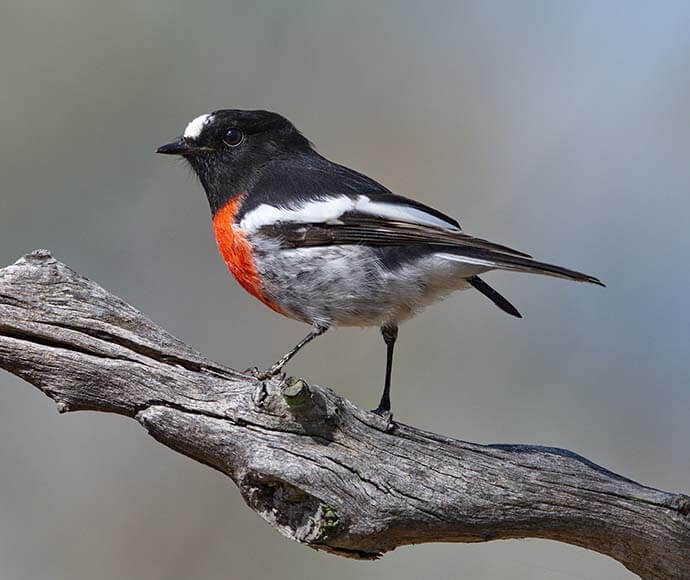
Several threatened bird species use the site and will benefit from the project, including the speckled warbler, scarlet robin and rose robin.
What will it be like to visit the park?
Yiraaldiya National Park will provide a visitor experience for the community of western Sydney and be a must-see destination for domestic and international visitors.
Visiting Yiraaldiya National Park will be like stepping back in time to see the Australian bush as it was before the arrival of foxes, cats and rabbits – to a time when the Australian bush was alive with native animals.
In the area previously used as a transmission station, there will be staged development of a visitor and education precinct. An education facility will provide a unique opportunity for visitors to learn about Australian native animals, the impacts of feral animals on their populations, the importance of protecting their remaining habitat and the role played by feral predator-free areas.
Recreation opportunities will include day-use facilities for picnicking and toilets, bushwalking, nature study and cycling. Camping and other accommodation facilities are planned to support research and educational activities.
What are the next steps?
Updates on the Yiraaldiya National Park feral predator-free area project will be published on this webpage as they occur.
Current park closures, fire and safety alerts
For the latest information on Yiraaldiya National Park and other park closures, fire and safety alerts:
- go to National Parks and Wildlife Service alerts
- call the National Parks and Wildlife Service on 1300 072 757 (13000 PARKS).
For the latest on road conditions related to this park, check the Live Traffic NSW website.
Updates













